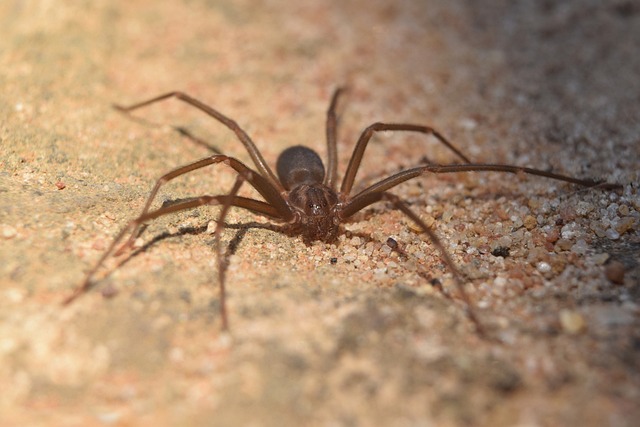
Executive Summary:
Common name: Corner, brown, recluse or fiddler spider
Habitat: Mainly found in urban and rural areas of Chile.
Venom: Highly toxic and potentially lethal, capable of causing severe skin injuries, tissue necrosis, and in extreme cases, death.
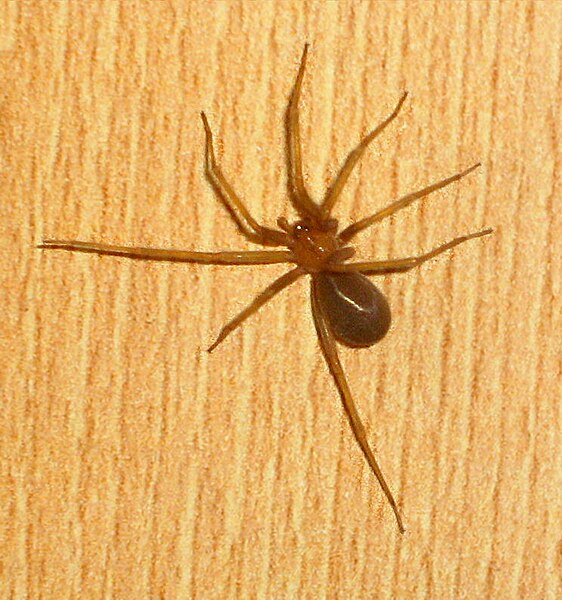
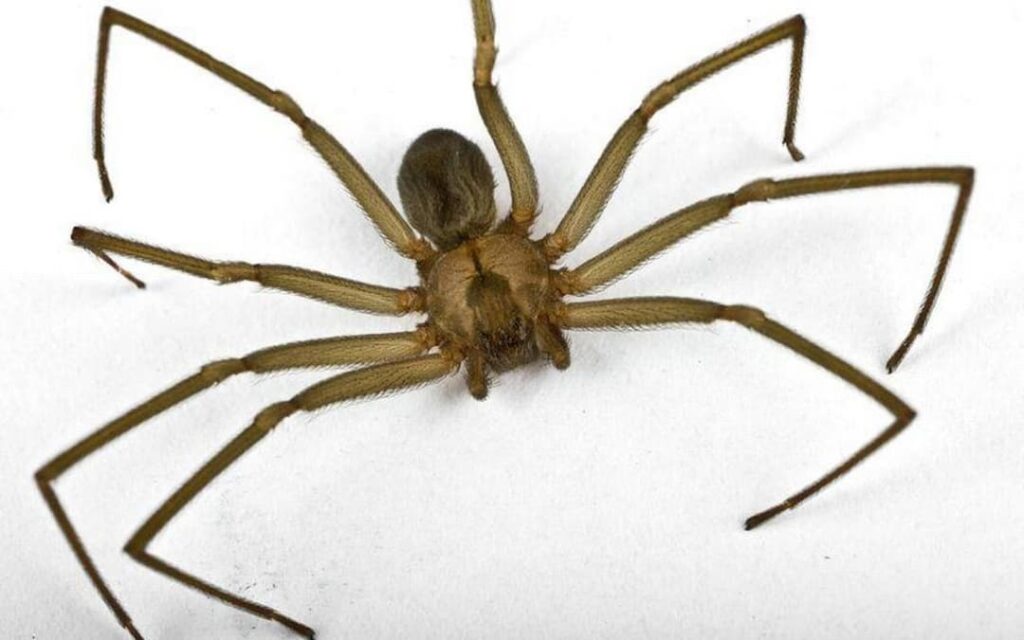
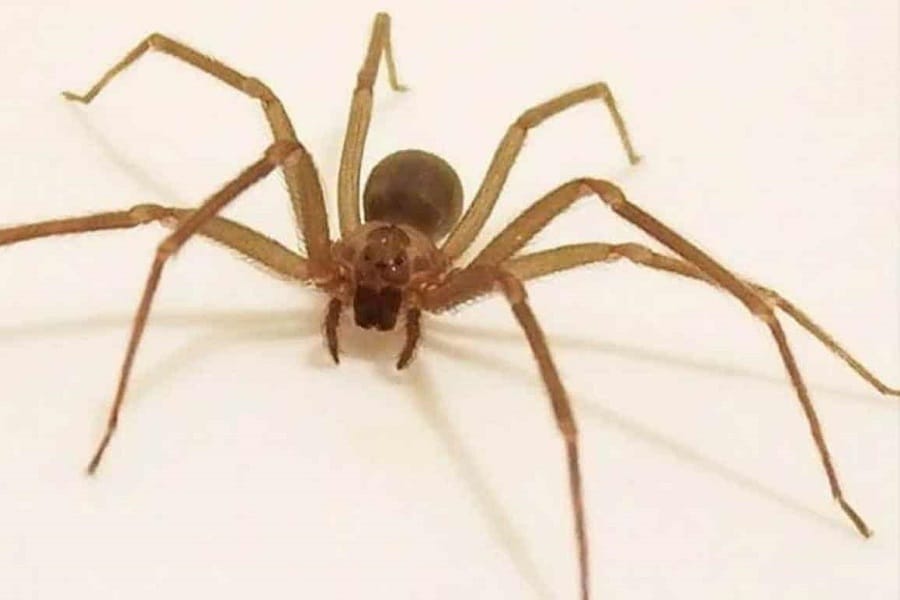
Appearance: Light to dark brown in color, with a distinctive violin-shaped mark on its back.
Habits: Non-aggressive, prefers to hide in cracks and dark corners.
Precautions: Avoid direct contact and seek immediate medical attention if bitten.
Introduction:
The brown recluse spider, also known as Loxosceles laeta, is a venomous species commonly found in Chile, especially in urban and rural areas. Despite its small size, this spider can pose a serious health risk to humans due to its highly toxic venom. In this post, we will explore in detail the biology, behavior, and precautions associated with the brown recluse spider.
Biology and Habitat:
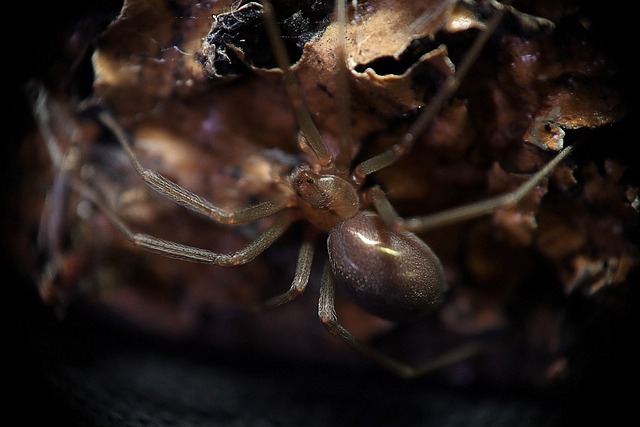
The Loxosceles laeta is a moderately-sized spider, with a body length ranging from 6 to 12 millimeters. Its color varies from light brown to dark brown, with a distinctive violin-shaped mark on its dorsal side, earning it the nickname “violin spider.” It prefers to inhabit dark and sheltered environments, such as cracks in walls, room corners, and similar spaces.
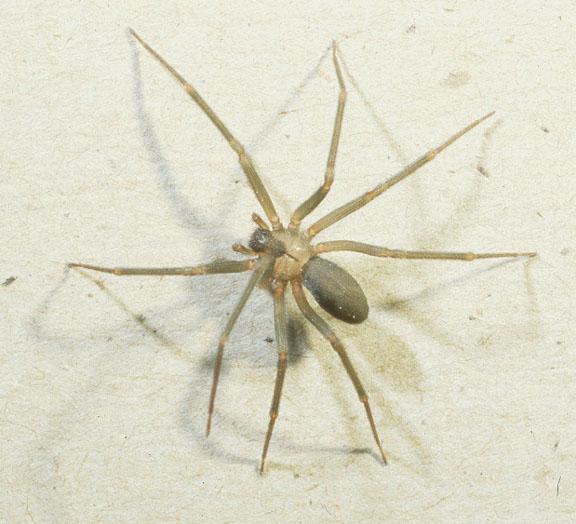

Venom and Dangers:
The venom of Loxosceles laeta is a highly harmful substance that can trigger a series of devastating effects on the human body. This spider is a master at camouflage and usually hides in dark and inaccessible places inside homes, thus increasing the risk of unwanted encounters with humans. One of its most disturbing characteristics is its ability to inoculate its venom without being detected, meaning that people can be bitten without even realizing it.
The venom of Loxosceles laeta is a lethal mixture of enzymes and toxins that have a devastating impact on human tissues. After the bite, victims may experience mild initial pain that can easily be mistaken for a common insect bite, delaying seeking appropriate medical attention. However, over time, the venom begins to corrode the surrounding tissue, causing deep, painful necrosis that can spread quickly if not treated effectively.
What is even more terrifying is that the venom of this spider can trigger a systemic response in the human body, leading to a series of serious complications and even death in extreme cases. Symptoms can range from severe abdominal pain to bleeding disorders and kidney failure, creating a nightmare scenario for those who suffer the bite.
It is crucial to note that the lethality of visceral cutaneous loxoscelism, the condition caused by the bite of this spider, is closely related to the speed in which it is diagnosed and the appropriate treatment is administered. Therefore, it is essential to monitor any type of loxoscelism during the first 24 to 48 hours after the bite, and to be alert for the appearance of symptoms and signs that suggest a possible visceral condition. The severity of a spider bite should not be underestimated, as lack of suspicion, monitoring or timely clinical treatment has been responsible for the majority of fatal cases recorded to date.
Images of the Devastating Damage Caused by Loxosceles laeta Venom
Caso 1
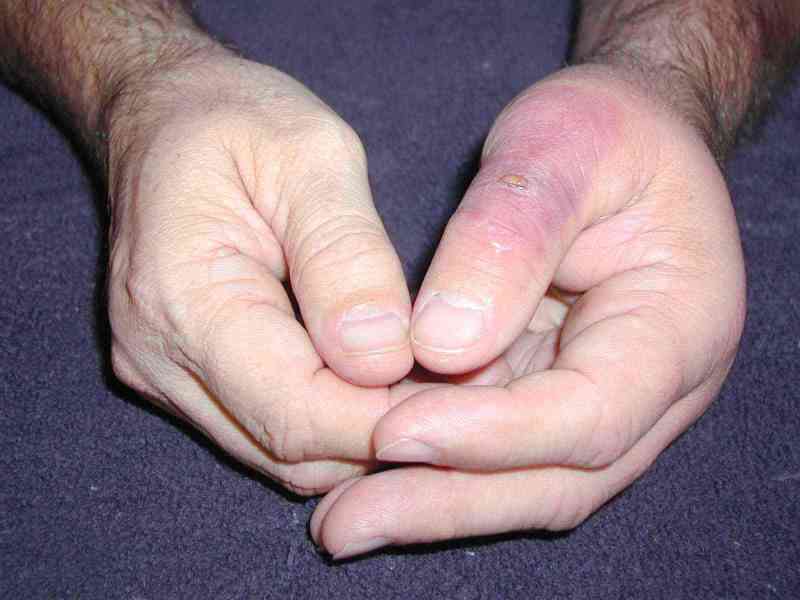
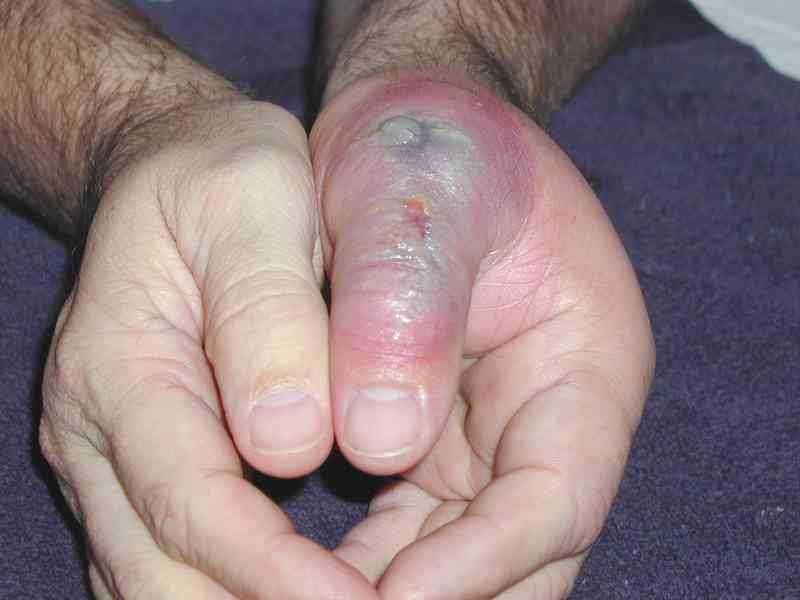
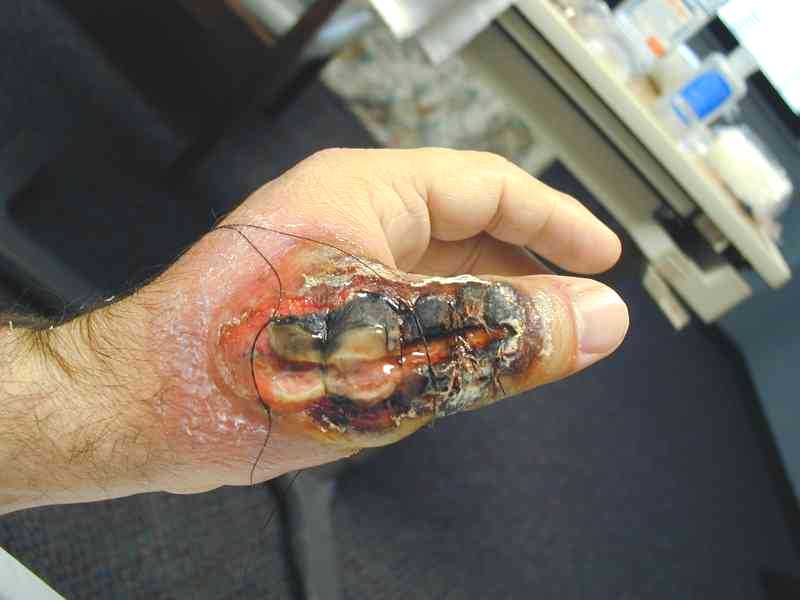
Caso 2
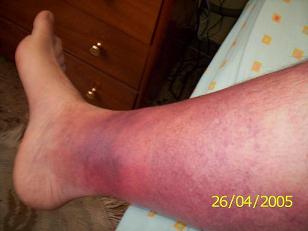
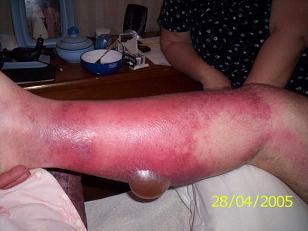
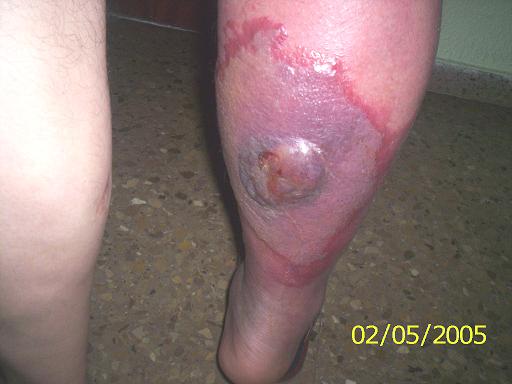
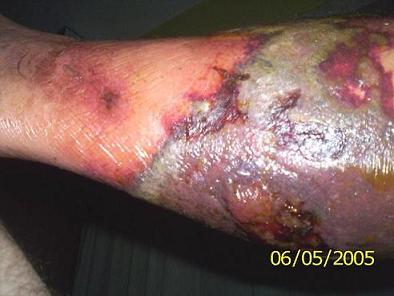
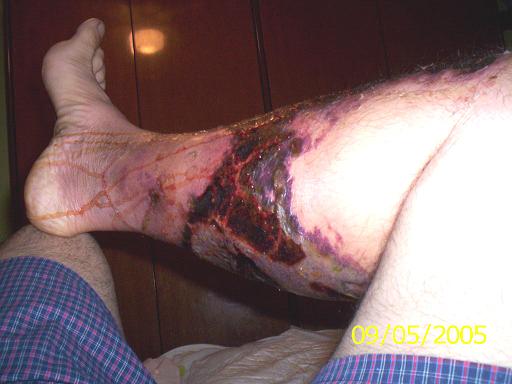
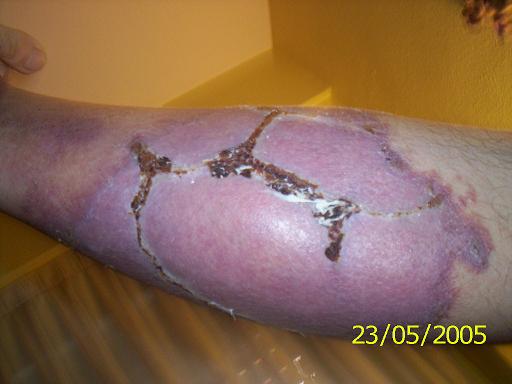
Behavior and Precautions:
While the Loxosceles laeta is not aggressive by nature, it may bite if it feels threatened or trapped. To minimize the risk of encountering these spiders, it is important to take preventive measures such as shaking out clothing before wearing it, regularly cleaning closets and storage areas, and inspecting behind pictures and furniture for signs of spider activity. When working in areas where brown recluse spiders may be present, the use of gloves and protective clothing is recommended to avoid direct contact with the spider. In the event of a bite, immediate medical attention should be sought to assess and properly treat the injury.
Preventive measures to avoid the bite:
- Maintain standards of cleanliness, hygiene and order in all spaces, including corners, behind and under furniture, pictures and books, as well as in the surroundings of buildings. Vacuum thoroughly periodically.
- Inspect the bed and corners before going to bed. Separate the beds 10 cm from the walls to prevent spiders from descending through them.
- Avoid hanging clothes or towels on the walls.
- Check and shake clothes and shoes before putting them on.
- Prevent children from playing inside closets or with boxes that have not been previously checked by a responsible adult.
- Eliminate access and habitat possibilities for spiders, closing holes and openings in walls, ceilings and floors.
- When entering a dark, dirty space or one that has been closed for a long time, do so with caution, shining a powerful flashlight and making noise to alert and give the spider time to move away.
- Use gloves and appropriate footwear to move objects that have been stacked or accumulated for a long time, such as boxes of clothing, construction materials.
- Avoid depositing materials or objects that favor the proliferation of domiciliary arthropods to reduce spider food.
- Domestic pesticides have low residual control and effectiveness through direct contact. It is recommended to use formulations with a spider effect and apply them in the dark and hidden places where Loxosceles resides and in the home, such as corners, closets or cellars. A microencapsulated formulation is suggested for residual control of spiders.
- Educate your family and close people about these topics.
Important measures in case of bite:
- Wash the wound with soap and water and let the affected limb rest.
- Remain calm and go immediately to the nearest Emergency Service.
- Do not step on or crush the animal as this makes it difficult to identify.
- Try to capture the offending spider to take it to the health center and identify it.
- If the spider causing the lesion is alive, it should be collected and kept in a container with a lid with cotton moistened with water.
- If the spider causing the injury is dead, it should be placed in a dry container.
- Even if the specimen is not in good condition, it is essential that you take it along with the injured person to the Emergency Service, from where it will be referred to an entomological study center. With this it will be possible to determine the species of spider.
Brown Recluse Spider photography




